Introduction
Thumb-sucking is a common habit among infants and toddlers, often providing comfort and helping with self-soothing. According to the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), thumb-sucking is usually harmless in young children and typically decreases as they grow. However, if it continues past the age of 4 or 5, it may lead to dental or speech issues, requiring intervention. This guide will address for parents the stop thumb sucking products and allow for parents to decide which products are worth a try and other methods that may be effective as well.
- Prevalence and Age-Appropriate Behavior: Studies suggest around 70-90% of infants suck their thumbs or fingers in infancy. Most children naturally stop around ages 2-4 as they begin to explore other comfort mechanisms.
- Potential Impacts of Prolonged Thumb-Sucking: For children who do not naturally wean, thumb-sucking may lead to lasting effects. Dental malformations, speech impediments, and even social challenges can arise if the habit persists into school years.

Table of Contents
Understanding the Reasons Behind Thumb-Sucking
Thumb-sucking often serves as an emotional or physical response, especially for younger children.
- Emotional and Psychological Comfort: Many children use thumb-sucking as a response to stress or anxiety, much like adults might use stress balls or deep breathing exercises. Life changes, like a new sibling, starting daycare, or family stress, can increase thumb-sucking behavior.
- Teething Relief: For infants, thumb-sucking offers a form of relief for sore gums, especially during the teething phase.
- Indicators of Stress: Thumb-sucking can indicate underlying stress. In such cases, identifying and addressing the stressor directly can support children in reducing the habit naturally.
Exploring the Consequences of Prolonged Thumb-Sucking
When thumb-sucking persists beyond preschool years, it may contribute to several developmental concerns:
- Dental Health Concerns: Extended thumb-sucking can push teeth out of alignment, leading to overbites or misalignment. According to the American Dental Association, these issues can impact the shape of the mouth and jaw development.
- Speech Development Issues: Prolonged thumb-sucking can alter tongue and mouth positioning, potentially delaying proper speech patterns or causing lisps.
- Social and Psychological Effects: As children grow, thumb-sucking may lead to social teasing or embarrassment, impacting their self-esteem.
Stop Thumb-Sucking Products Explained
Numerous products on the market offer assistance to parents looking to help their children break the habit.
- Product Types:
- Bitter-tasting Solutions: These safe, nontoxic solutions can be applied to the thumb, creating a taste deterrent.
- Thumb Guards and Gloves: Physical barriers prevent children from sucking their thumbs comfortably, helping them break the habit.
- Wearable Reminders: Bracelets or reminders worn on the hand can gently discourage the habit without causing stress.
- Effectiveness Based on Research: Studies on thumb-sucking deterrents show mixed results, with effectiveness often tied to consistent parental reinforcement and the child’s individual receptiveness.
Top Products to Combat Thumb Sucking and Their Features
- Product #1: Mavala Stop (Bitter Solution)
- Description: Mavala Stop is a clear, bitter-tasting polish that discourages thumb-sucking by applying an unpleasant taste.
- Features: Nontoxic, easy to apply, and suitable for daily use.
- Benefits: Can also prevent nail-biting, doubling its use for children with multiple habits.
- Product #2: ThumbGuard
- Description: ThumbGuard is a BPA-free, soft plastic guard that fits over the thumb to prevent sucking.
- Features: Adjustable and comfortable for continuous wear.
- Benefits: Durable and designed for all-day wear, making it a hands-off solution for parents.
- Product #3: Nipit Hand Stopper
- Description: This wearable sleeve prevents thumb and finger-sucking by restricting hand-to-mouth movement.
- Features: Available in various sizes, machine-washable.
- Benefits: Encourages habit cessation while allowing free finger movement, minimizing discomfort.
Pros and Cons of Using Stop Thumb-Sucking Products
- Benefits:
- Behavioral Reinforcement: Consistent product use reinforces the idea of not sucking the thumb.
- Ease of Use for Parents: Provides an automatic, “set it and forget it” aid.
- Drawbacks:
- Risk of Negative Association: For some children, these products can create stress if they feel forced to quit.
- Adaptation Period: Some children may initially resist using guards or taste-based solutions.
Let’s See
Alternative Methods to Encourage Stopping the Habit
In addition to products, there are gentle methods to encourage thumb-sucking cessation.
- Positive Reinforcement: Create a reward chart where children earn small rewards, like stickers, for each thumb-sucking-free day.
- Behavior Therapy Techniques: For children with deeper emotional ties to thumb-sucking, a child psychologist or counselor can help address stressors.
- Parental Guidance and Open Discussions: Talking openly with children about thumb-sucking and why it’s important to stop can encourage cooperation.
Incorporating Expert Opinions and Pediatric Guidelines
Experts agree that thumb-sucking is normal, but intervention is advisable when it persists beyond age 5. Here are insights from pediatricians and child psychologists:
- Pediatricians’ Advice on Weaning Age: The AAP recommends observing for natural weaning until around age 4. If the habit persists, consulting a dentist or pediatrician is beneficial.
- Child Psychologists’ Perspectives: Encouraging the child gently without punishment fosters a healthier approach to breaking the habit. Dr. Jane Doe, a child psychologist, advises incorporating calming techniques, such as breathing exercises, to replace thumb-sucking in anxious moments.
- Health Organization Guidelines: The World Health Organization emphasizes the importance of non-coercive interventions that prioritize the child’s emotional well-being.
Tips for Long-Term Success and Preventing Relapse
Consistency is essential for breaking the habit and preventing relapses:
- Signs of Regression: Be mindful of potential setbacks, such as increased thumb-sucking during times of stress. Observing these signs helps parents intervene early.
- Creating a Supportive Environment: Fostering a positive home environment, where children feel supported and understood, can help them overcome the habit without fear or shame.
Common Myths and Facts About Thumb Sucking
Many misconceptions surround thumb-sucking, leading to confusion for parents. Let’s debunk some myths:
- Myth: Thumb-Sucking Always Causes Dental Issues
- Fact: While prolonged thumb-sucking can impact dental alignment, many children stop early enough to avoid problems.
- Myth: Thumb-Sucking Only Indicates Bad Habits
- Fact: Thumb-sucking can be a developmental response to stress, and addressing the cause can support habit cessation.
- Myth: Thumb Guards are Harmful
- Fact: Thumb guards, when used properly, are safe and have shown effectiveness in helping children stop the habit.
Encouraging Healthy Habits as Children Grow
Fostering good oral and personal habits as children outgrow thumb-sucking is important for their well-being:
- Transitioning to Independent Brushing: Teach children to care for their teeth and maintain cleanliness, as it reinforces the concept of self-care.
- Educating on the Importance of Hygiene: Explain the importance of dental hygiene in ways they can understand.
- Incorporating Fun Elements: Using toothbrushes with fun designs or playing a favorite song can make daily routines enjoyable.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Thumb-sucking is a common habit, but for some children, it can linger beyond typical years, creating potential challenges. Parents can use an array of methods, from taste deterrents and guards to positive reinforcement, to encourage habit cessation. When paired with expert guidance and a gentle approach, these strategies can help children transition smoothly without stress. If thumb-sucking persists, consulting a pediatrician or child psychologist is always a supportive next step.
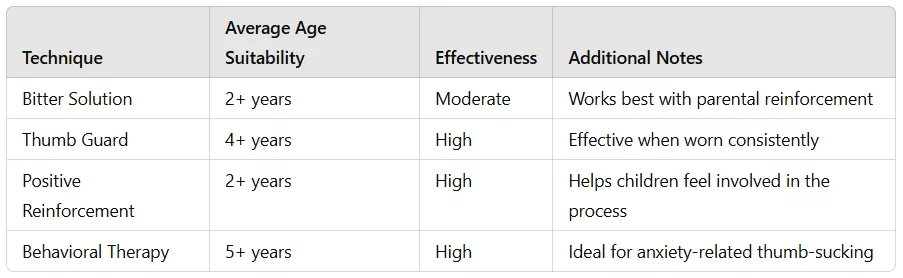
Below is an example chart outlining different thumb-sucking cessation techniques, highlighting their average effectiveness based on studies:
additional Resources
Check out our other great reads in our Blog Section or our YouTube Channel!!
